

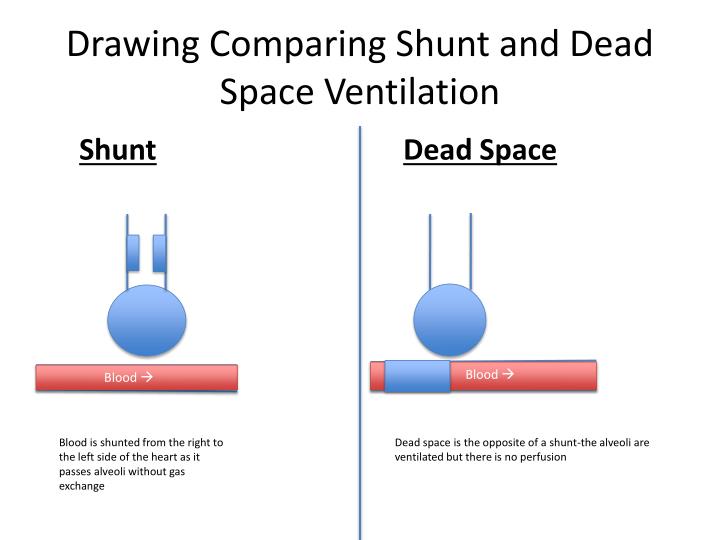
Anatomic Dead SpaceĪnatomic deadspace consists of the parts of the respiratory tract that are ventilated but not perfused. They all impact how well a patient ventilates. There are three types of dead space: anatomic, physiologic, and that dead space belonging to any airway equipment being used to assist ventilation. Dead space is the portion of the respiratory system where tidal volume doesn’t participate in gas exchange: it is ventilated but not perfused. One important contributor to ventilation perfusion mismatch is dead space.

It will help you understand how you can use these concepts to care for your patient. This article will describe how dead space is different from shunt. Physiologic dead space is ventilation of poor perfused alveoli. Mark S Siobal Respir Care 2016 61: (c) 2012 by Daedalus Enterprises, Inc.Shunt is perfusion of poorly ventilated alveoli. Also shown are PaCO2, the partial pressure of venous carbon dioxide (PvCO2), the relationship between PaCO2 and minute CO2 production (V̇CO2) and alveolar gas volume, the partial pressure of mixed alveolar carbon dioxide (PACO2), the partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide (PETCO2), and the PĒCO2 in relation to the model and the volumetric capnogram.

The dead space fraction is equal to VDphys divided by tidal volume (VT). The sum of the regions of alveolar dead space (VDalv) and anatomic dead space (VDanat) equal the physiologic dead space (VDphys). The pure dead-space compartment represents areas of ventilation with no perfusion. The pure shunt compartment represents areas of perfusion without ventilation. The ideal compartment represents areas of perfect alveolar gas volume to Q̇T matching. The 3-compartment lung model described by Riley and Cournand151,152 represents gas exchange in the lung in regard to the matching of alveolar gas volume (V̇A) and perfusion (Q̇T), shunt (Q̇S), and dead space (VD). Presentation on theme: "The 3-compartment lung model described by Riley and Cournand151,152 represents gas exchange in the lung in regard to the matching of alveolar gas volume."- Presentation transcript:ġ The 3-compartment lung model described by Riley and Cournand151,152 represents gas exchange in the lung in regard to the matching of alveolar gas volume (V̇A) and perfusion (Q̇T), shunt (Q̇S), and dead space (VD).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
